Norepinephrine – What Is It And What Is It For?
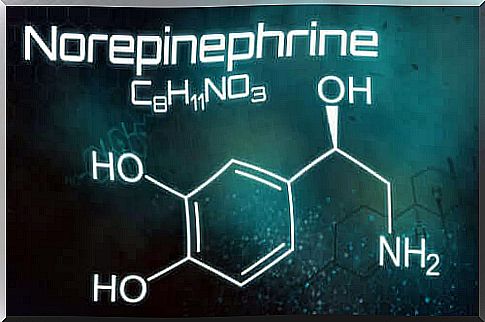
Norepinephrine, also known as norepinephrine, is an adrenergic neurotransmitter. It is a catecholamine synthesized in the body from the amino acid tyrosine.
This neurotransmitter is synthesized in the adrenal glands and postganglionic neurons of the sympathetic and central nervous systems. But how does norepinephrine affect the body?
How does norepinephrine affect the body?
Norepinephrine binds to adrenergic receptors to trigger its action in the body. These receptors can be divided into two groups: α receptors (of which two subtypes are known: α1 and α2) and β-adrenergic receptors in which there are three subtypes.
The adrenergic reaction is activated when a person is in danger or a stressful situation. This is a perfectly normal body response. It is based on the fact that the central nervous system sends a series of signals through the sympathetic nervous system to various organs.
In the kidney glands, this system is able to stimulate the synthesis and release into the blood of both epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline). Thanks to this, these two substances are properly distributed throughout the body.
Usually more adrenaline is released than norepinephrine, roughly in a proportion of 80–20%. When they reach different organs and bind to the appropriate receptors, a series of reactions are triggered, causing the characteristic activation effects of these receptors to occur.
Let’s see below what physiological effects norepinephrine has on various organs.
Norepinephrine is released into the blood so that it can travel easily and reach different organs. Its job is to trigger their reaction. And so, in the respiratory system, it causes the airways to widen to make it easier to breathe in a stressful situation.
In the blood vessels, in turn, it causes vasoconstriction, and in the heart, a characteristic increase in heart rate. These physiological effects try to increase the flow of oxygen and blood to the major muscle groups. This means that in a situation of stress or danger, our body properly prepares to react better.
In addition to the above-mentioned activities, norepinephrine also affects metabolism. It affects both the secretion of insulin and the release of fat stores. However, it has even more effects in this area, not only the two mentioned.
Moreover, this neurotransmitter has significant effects on the attention, alertness, and reward system in the brain. Due to its action on the central nervous system, norepinephrine functions rather as a neurotransmitter. So it is not considered a hormone as is the case with adrenaline.
However, when it is released into the circulation and exerts an effect on cells from a distance, it acts as a hormone. On the other hand, when it interacts between two adjacent cells, it acts as a neurotransmitter.
Uses of norepinephrine
Norepinephrine can be used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, as well as in depression and hypotension.
Norepinephrine in the treatment of attention deficit disorder
Along with dopamine, norepinephrine plays an important role in both focus and concentration. For this reason, patients with attention deficit disorder are usually treated with psychostimulants.
Methylphenidate is administered to increase the levels of norepinephrine and dopamine in the brain and thus improve the clinical picture of this disorder.
Depression and norepinephrine
Serotonin reuptake inhibitors or SSRIs also increase the amount of norepinephrine in the presynaptic space. However, they are not fully selective for this neurotransmitter,
Research indicates that these drugs also affect dopamine transmission. So, if the norepinephrine transporter normally produces any dopamine molecules, then these drugs will also improve dopaminergic transmission.
Thus, the antidepressant effect associated with the increased level of norepinephrine may also result from a concomitant increase in dopamine.
Hypotension
Due to its strong vasoconstrictor action, norepinephrine is recommended for patients at critical risk of hypotension. For this purpose, it is administered intravenously. In this case, the activation of α 1 and α 2 receptors is responsible for inducing these effects.
Application
Norepinephrine, also known as norepinephrine, is a neurotransmitter that is released especially when we are under stress or distress. It works the same as adrenaline, but mainly at the level of the central nervous system. Therefore, it is considered a neurotransmitter and not a hormone.